Product
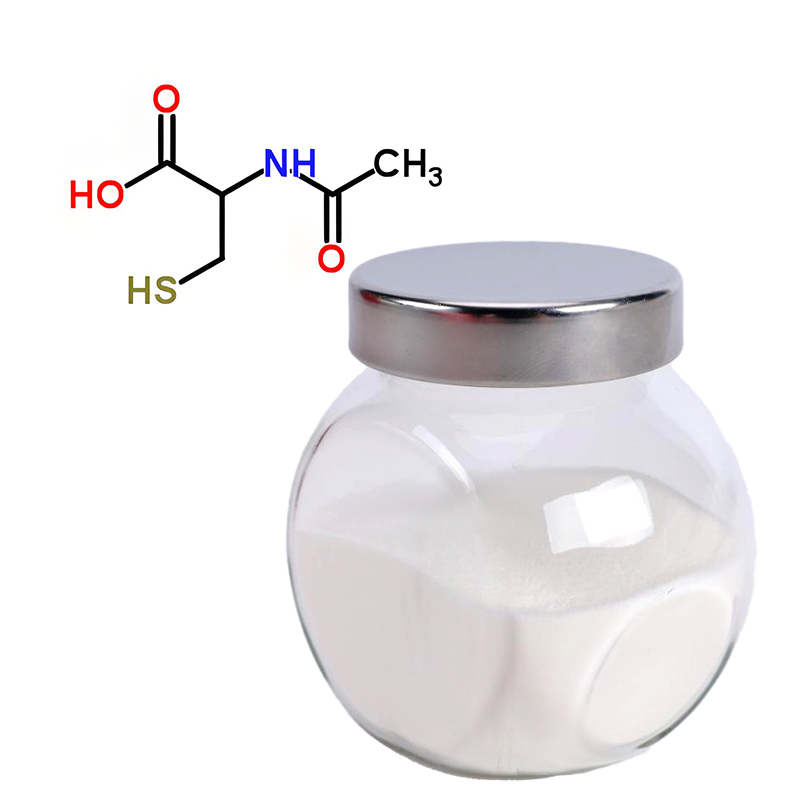
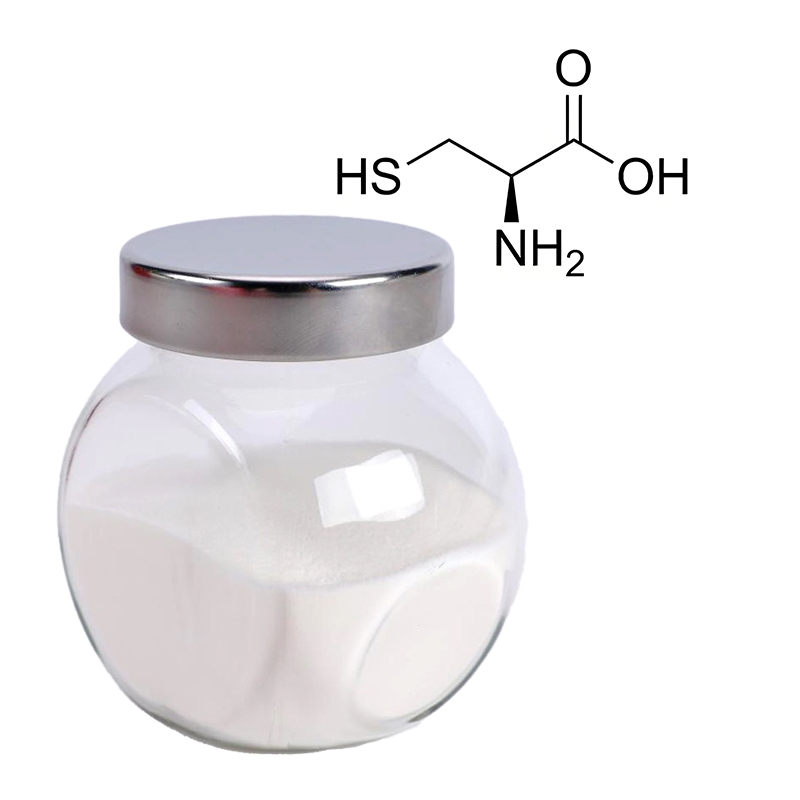
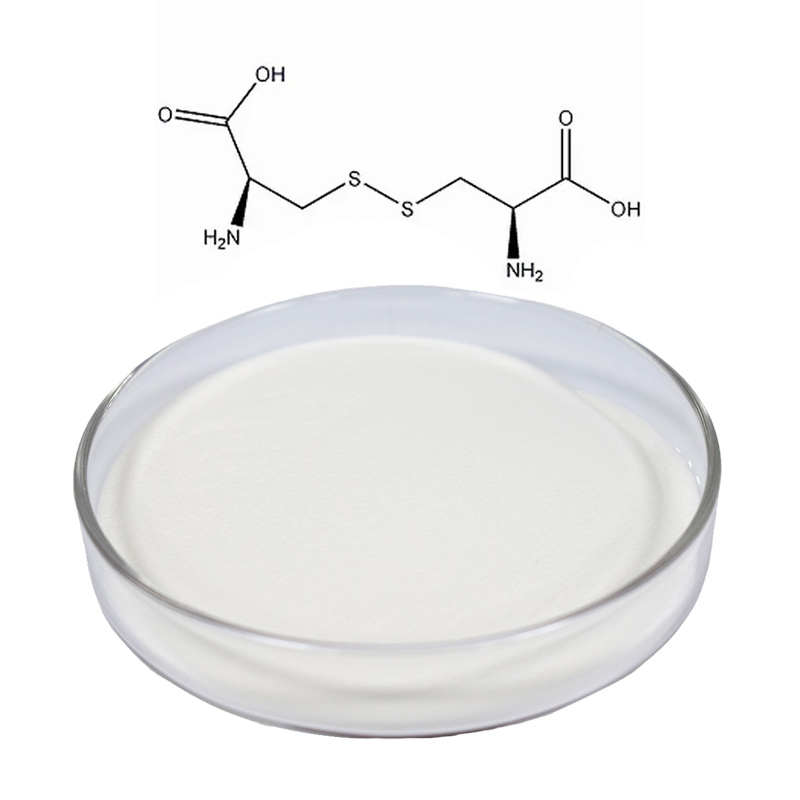
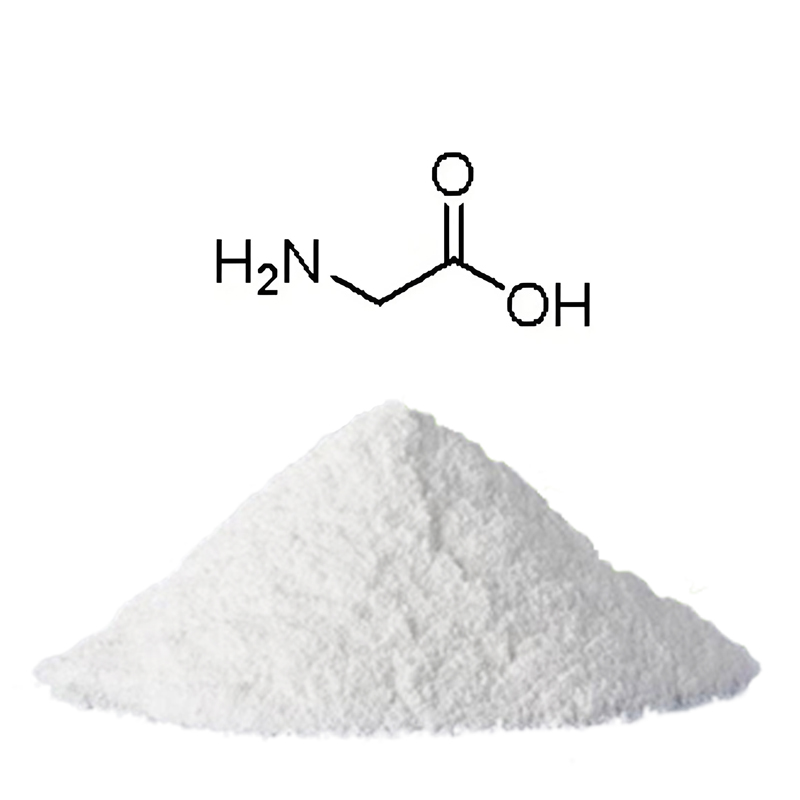
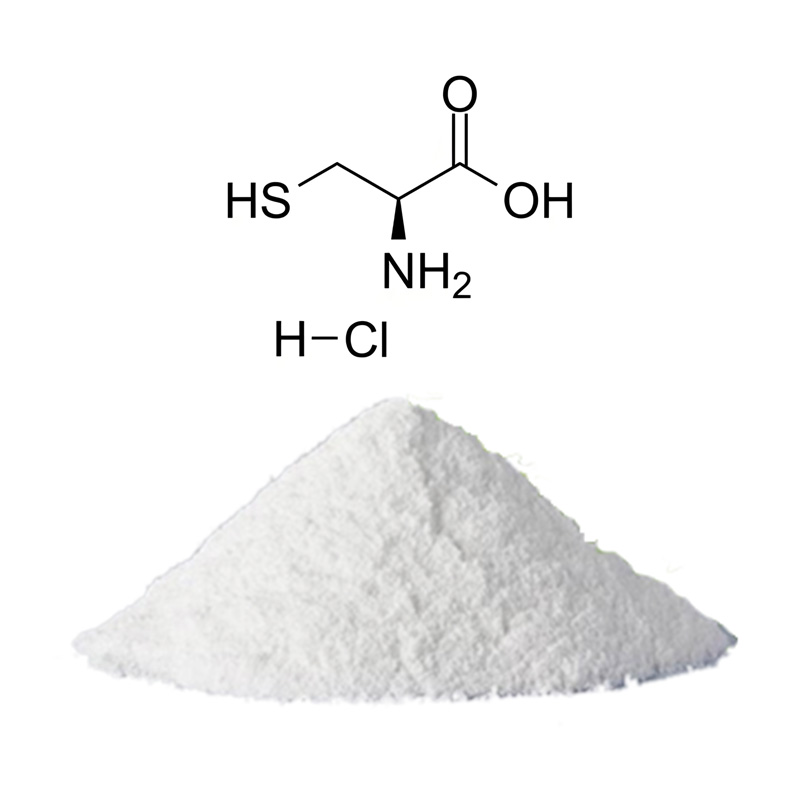
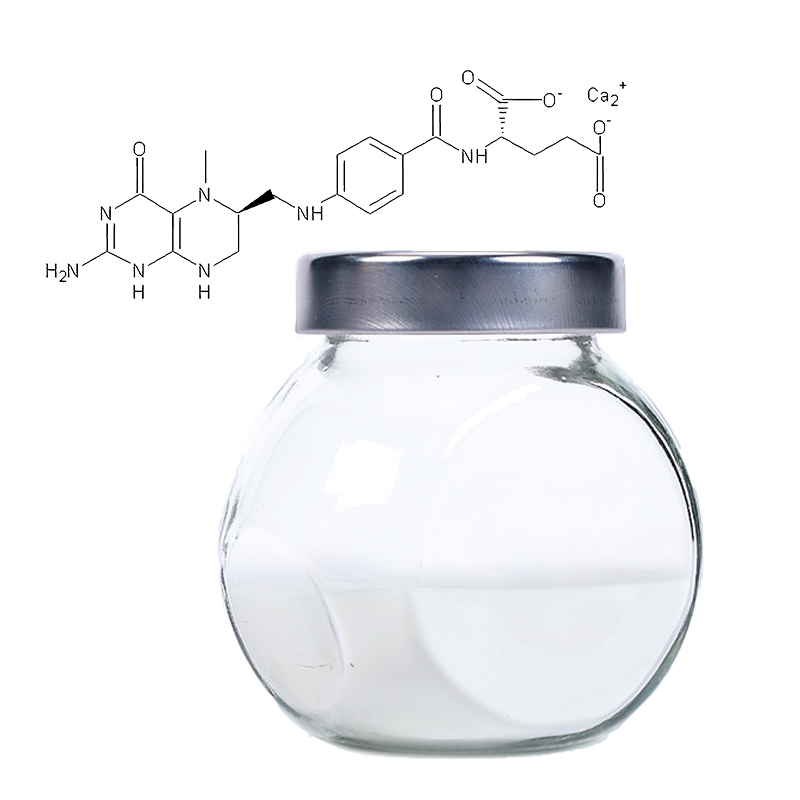
S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine
Common Name: Carbocysteine
CAS Number: 638-23-3
Purity: 98.5%-101.0% by HPLC
Описание
маркер
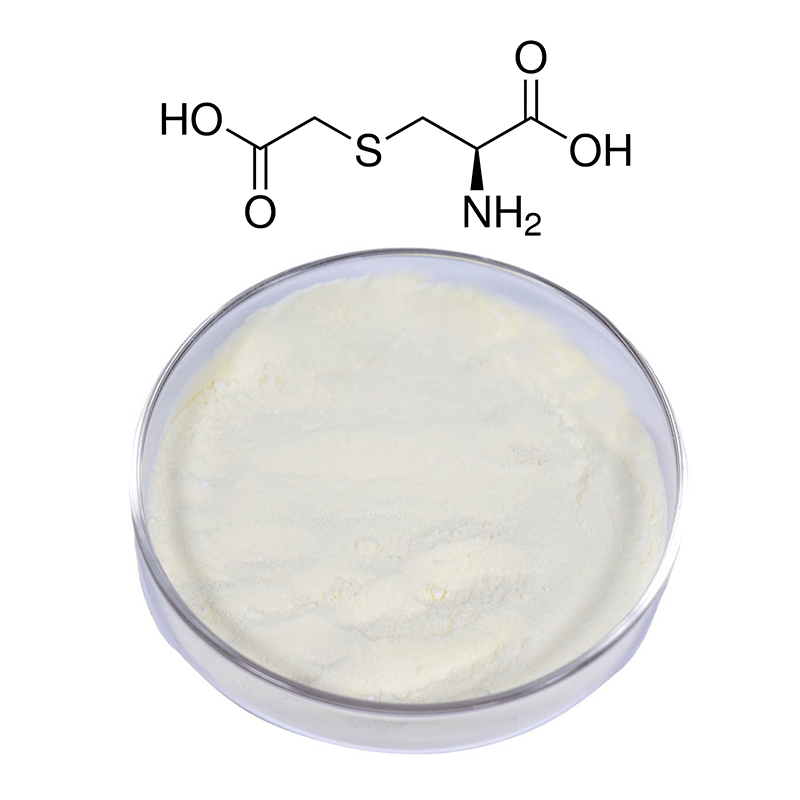
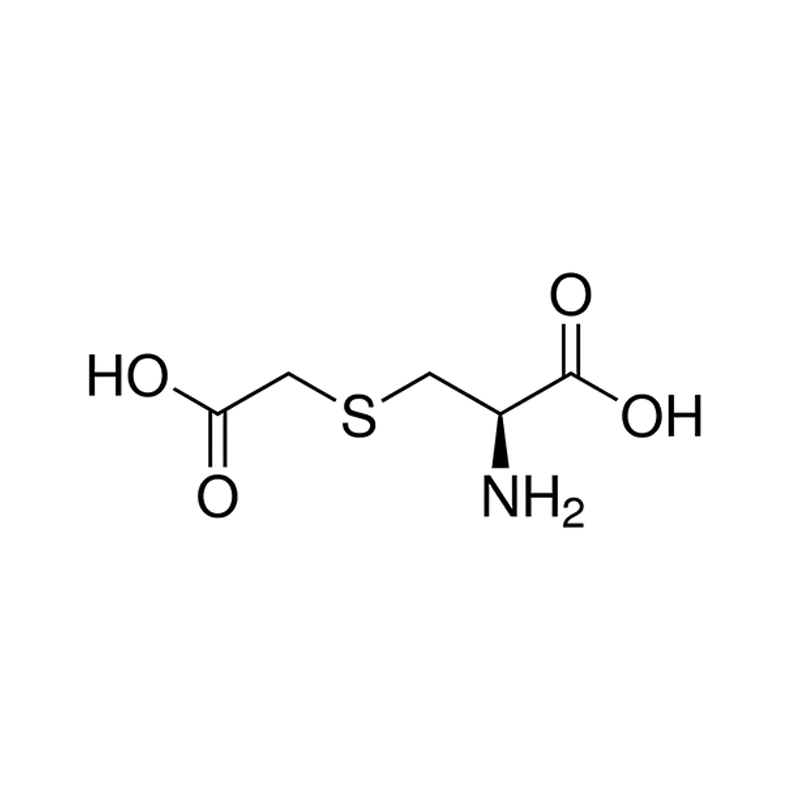
S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine
Common Name: Carbocysteine
CAS Number: 638-23-3
Purity: 98.5%-101.0% by HPLC
Overview
S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine (commonly known as Carbocysteine) is a respiratory mucolytic agent that is used to treat various pulmonary conditions. It is an amino acid derivative, specifically a modified form of cysteine, that acts to reduce mucus viscosity and promote the easier expulsion of mucus from the respiratory tract. This substance is similar in its function to other mucolytics like bromhexine, but with a distinct biochemical mechanism.
Function and Mechanism of Action
Carbocysteine works primarily by breaking disulfide bonds in the mucoproteins (mainly mucin) present in mucus. By cleaving these bonds, it reduces the viscosity of the mucus, making it less sticky and easier to expel through coughing. The following are the key ways in which Carbocysteine works:
- Reduction in Mucus Viscosity: Carbocysteine promotes the breaking of disulfide bonds in mucoproteins, which helps to lower the viscosity of the mucus, making it easier to clear from the airways.
- Increased Mucus Secretion: The drug also enhances the secretion of low-viscosity mucus, which further facilitates the clearance of thickened mucus.
- Improvement in Ciliary Function: Carbocysteine can also help to improve ciliary function, aiding in the movement of mucus from the lungs to the throat, where it can be coughed up.
The mechanism of action is akin to that of bromhexine, but Carbocysteine is generally considered more specific for breaking down mucin (a glycoprotein) in mucus. As a result, it is particularly useful in conditions where thick and sticky mucus obstructs the airways.
Therapeutic Uses
Carbocysteine is used primarily as a treatment for conditions associated with thick and difficult-to-clear mucus in the respiratory system. Some of the main indications include:
- Chronic Bronchitis: A long-term inflammation of the bronchi, often caused by smoking or infections, which results in excessive mucus production and difficulty clearing it from the airways.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A group of lung diseases that block airflow and make breathing difficult. Carbocysteine helps in reducing mucus viscosity, which is a common issue in COPD patients.
- Asthma: Particularly in cases where mucus overproduction is contributing to respiratory obstruction.
- Bronchial Asthma: In combination with bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory treatments, Carbocysteine helps reduce the viscosity of mucus, facilitating easier breathing and reducing airway blockage.
Benefits of Carbocysteine
- 1.Mucolytic Action: It helps in thinning and loosening mucus, making it easier to expel.
- 2.Reduction of Mucus Blockages: By reducing the viscosity of mucus, Carbocysteine aids in preventing blockages in the airways.
- 3.Improved Respiratory Function: Patients often experience improved airflow and reduced coughing due to easier mucus expulsion.