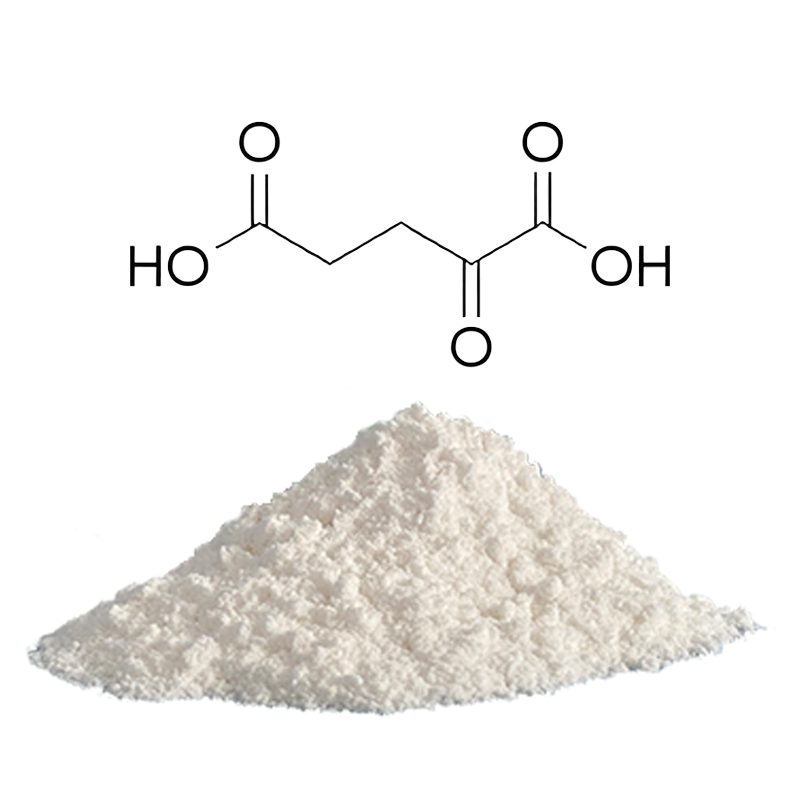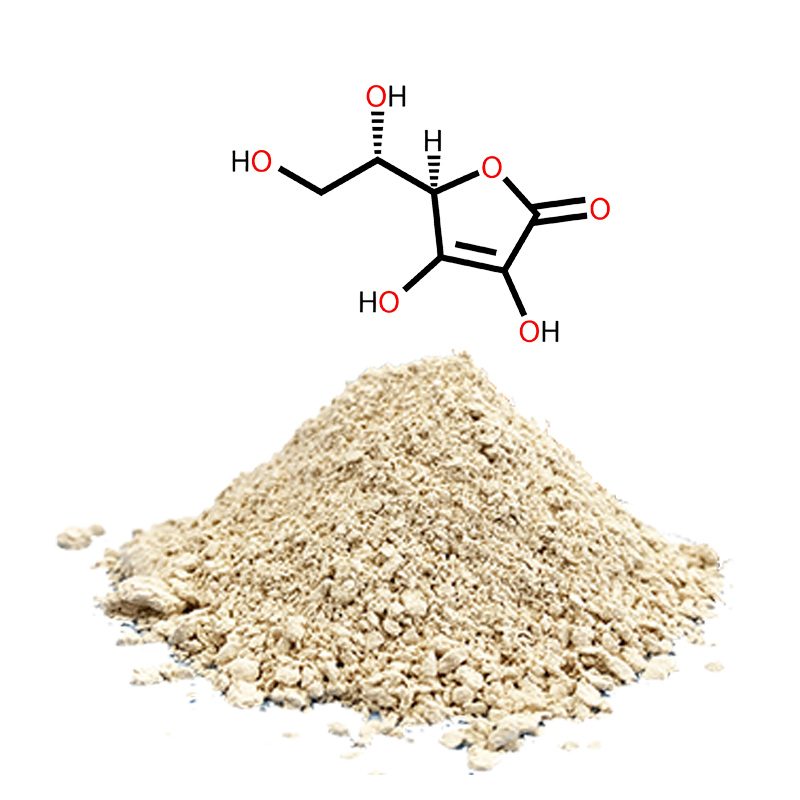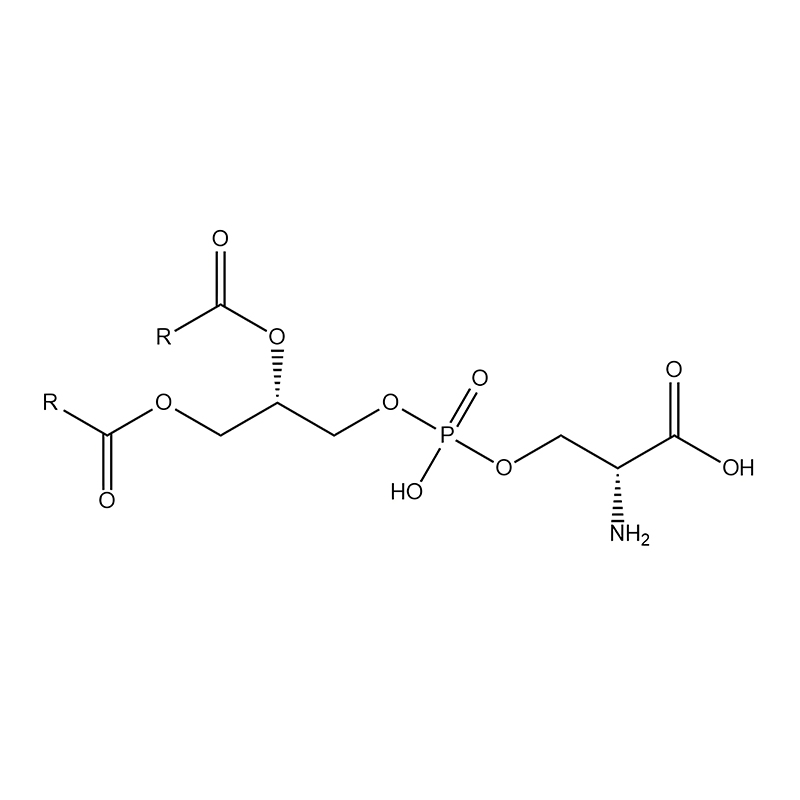
Product
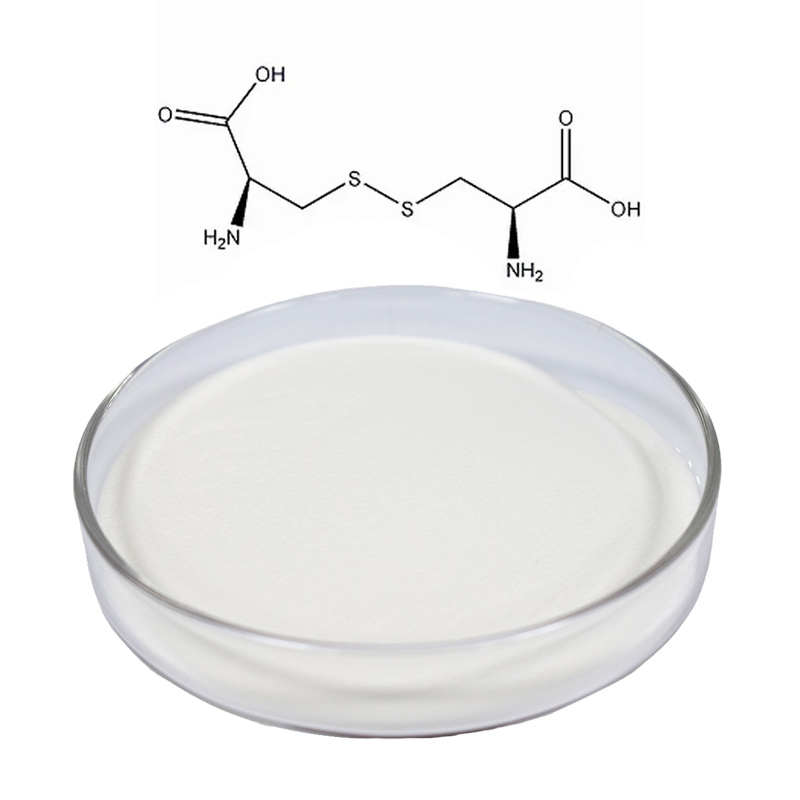
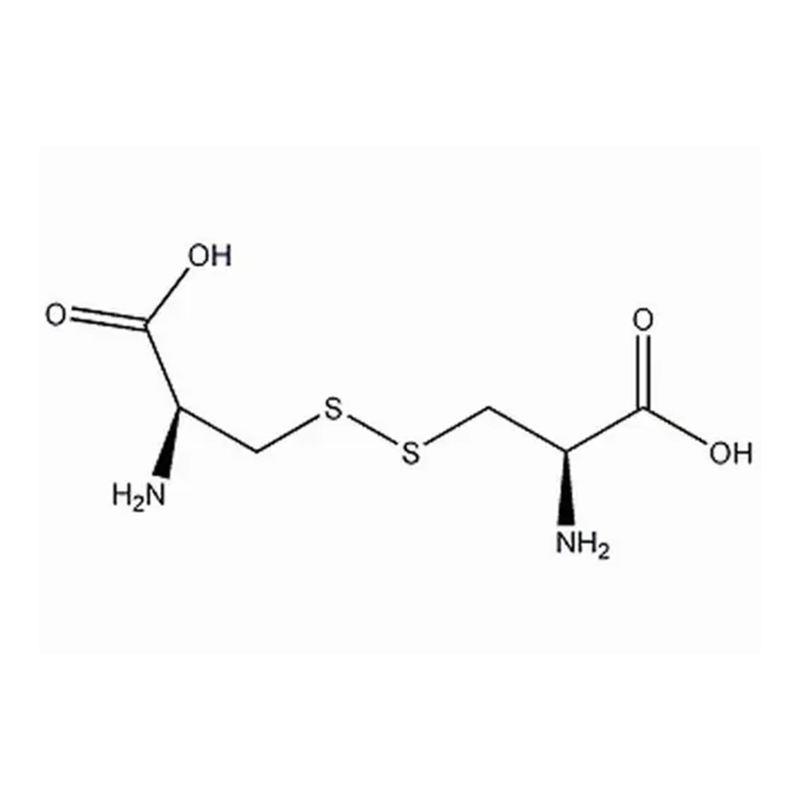
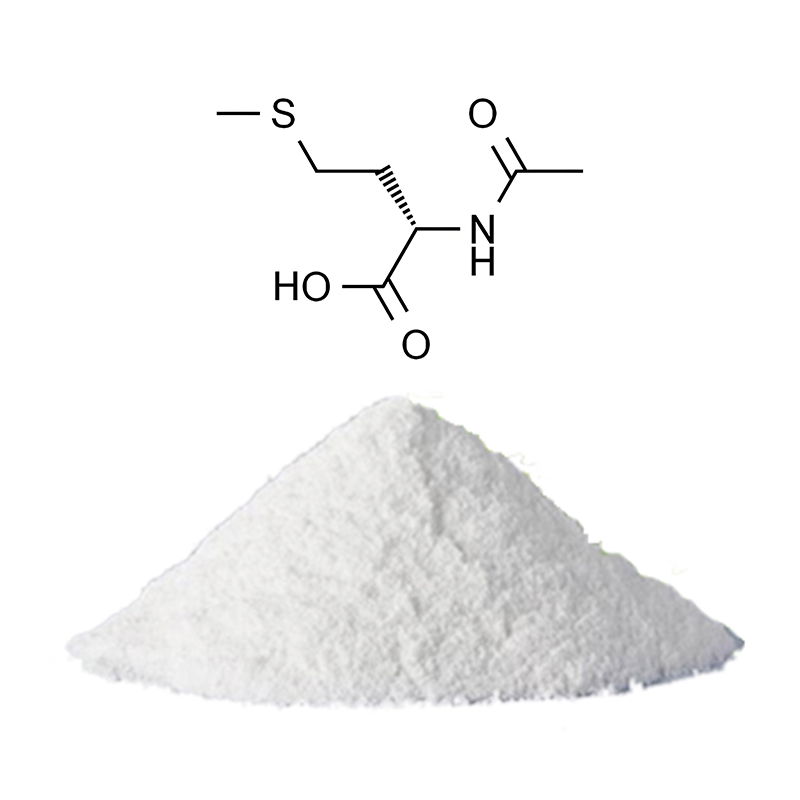
L-Cystine
CAS Number: 56-89-3
Molecular Formula: C₆H₁₂N₂O₄S₂
Molecular Weight: 240.3 g/mol
Specification: 98.5%-101.0% by HPLC
Описание
маркер
L-Cystine
CAS Number: 56-89-3
Molecular Formula: C₆H₁₂N₂O₄S₂
Molecular Weight: 240.3 g/mol
Specification: 98.5%-101.0% by HPLC
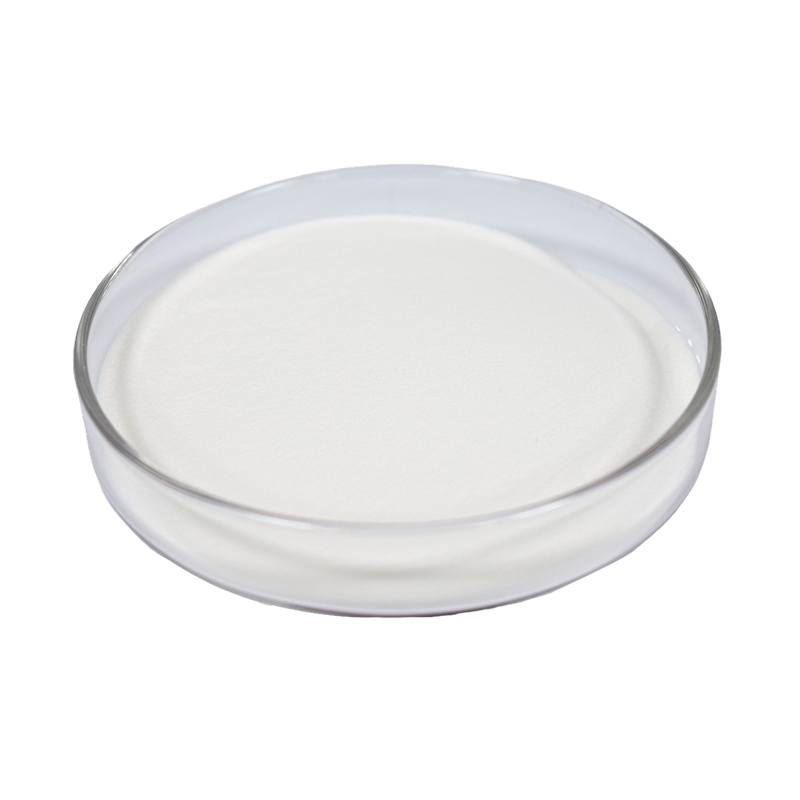
Appearance: White hexagonal plate-like crystals or white crystalline powder
Solubility: Soluble in dilute acids and alkali solutions, very slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol
L-Cystine is an organic compound that plays several important roles across multiple industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics. It exists in trace amounts in proteins, especially in keratins such as those found in hair and nails. Below, we explore its various uses and characteristics.
Characteristics of L-Cystine
- 1.Chemical Structure and Physical Properties
L-Cystine is composed of two cysteine molecules linked by a disulfide bond. The molecule features sulfur atoms, which contribute to its biological and chemical reactivity. The compound appears as white crystals, commonly in a hexagonal shape, and is a key component in the synthesis of various proteins, particularly keratin (present in hair and nails). - 2.Solubility
L-Cystine is soluble in dilute acids and alkalis but shows minimal solubility in water and ethanol. This makes it a useful compound for various applications where its interaction with aqueous solutions is limited, such as in certain pharmaceutical formulations. - 3.Molecular Function
As a dimer of cysteine, L-cystine is vital for the formation of disulfide bonds in proteins, contributing to their structural integrity. These bonds are essential in stabilizing the three-dimensional structure of proteins, particularly in the synthesis of keratin found in hair, nails, and skin.
Applications of L-Cystine
- 1. Pharmaceutical Use
L-Cystine is a precursor for producing detoxifying agents and expectorants. It helps in breaking down mucus in the lungs, making it useful for treating respiratory conditions. Its role in neutralizing toxins within the body further enhances its importance in medicinal formulations. Additionally, it is involved in producing antioxidants, due to its sulfur-containing structure that participates in redox reactions.
- 2. Food Industry
L-Cystine is used in food production as an additive in dairy products and bread-making. It acts as a bread improver, enhancing the texture and elasticity of dough. L-Cystine also reacts with sugars when heated, producing various distinct aromas that are desirable in food preparation. This property makes it valuable in creating special flavors in food items like baked goods and dairy products. Furthermore, it helps prevent fat oxidation, ensuring longer shelf life and maintaining the quality of food items during storage.
3. Cosmetic Use
In cosmetics, L-Cystine is primarily used as a raw material for cold perm solutions. Its role in the formation of disulfide bonds in hair makes it essential in products that alter hair texture, such as hair straightening and perming formulations. This is due to its ability to break and re-form the disulfide bonds that define hair’s natural shape.
4. Industrial Applications
Beyond pharmaceuticals and food, L-Cystine finds various industrial applications due to its role as a reducing agent and its sulfur-containing structure, which interacts with other chemicals in specific industrial processes.