Product
-

Marigold flower Extract
-
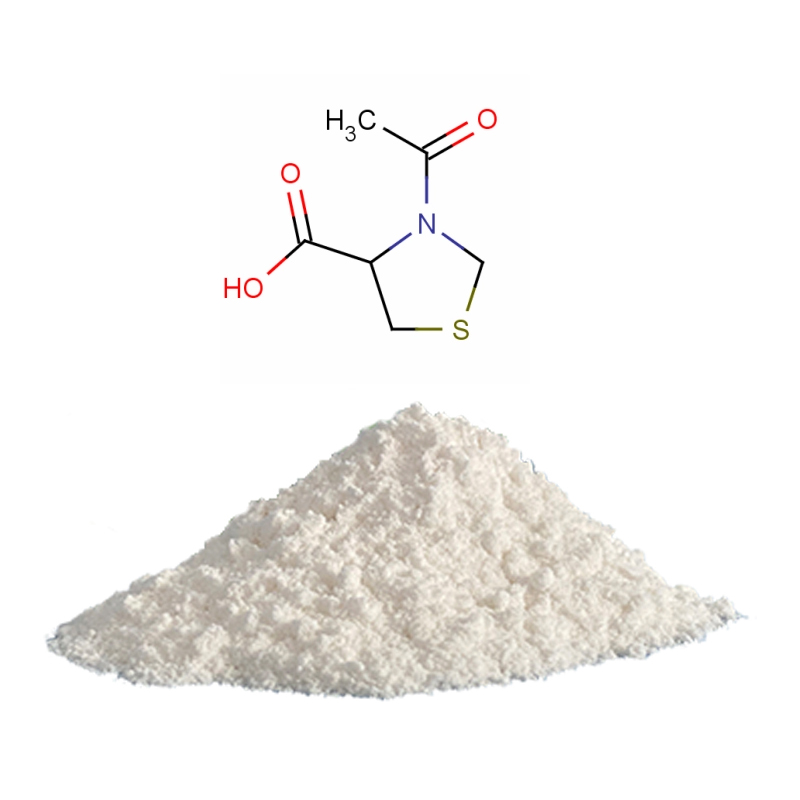
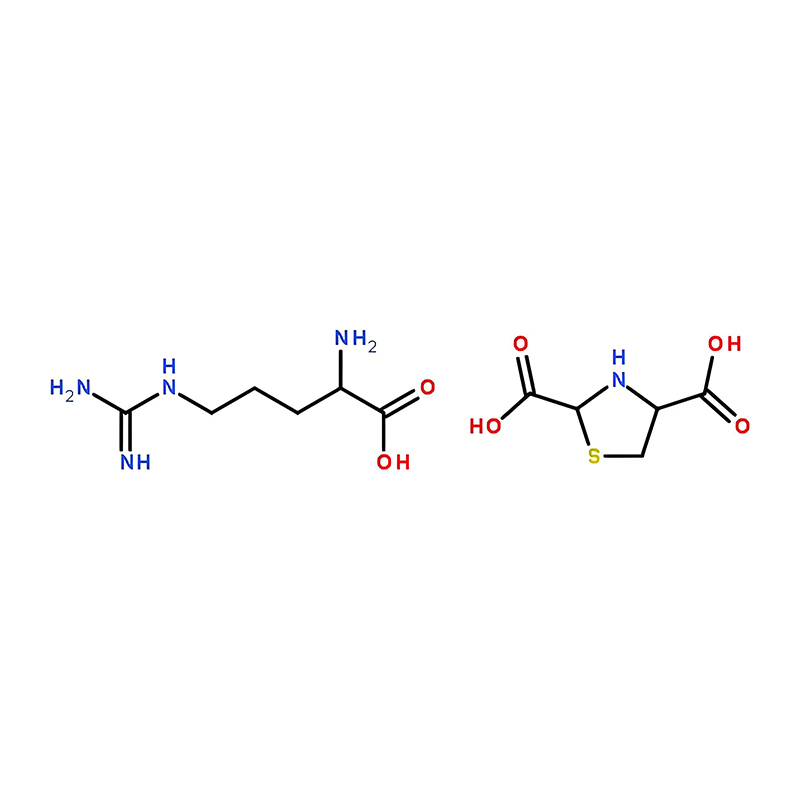
N-Acetyl Thioproline
-
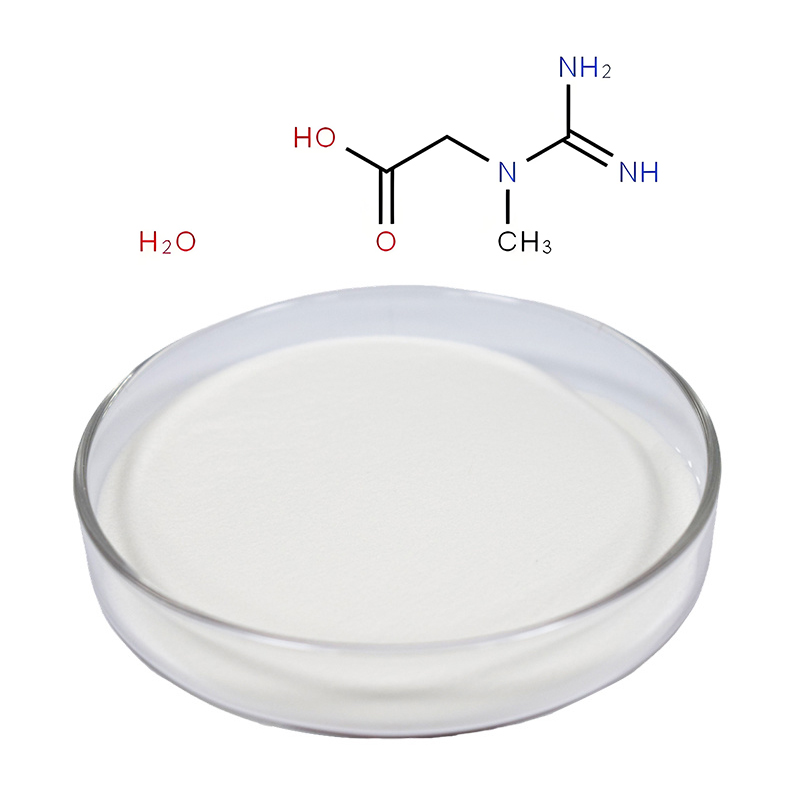
Creatine Monohydrate
-
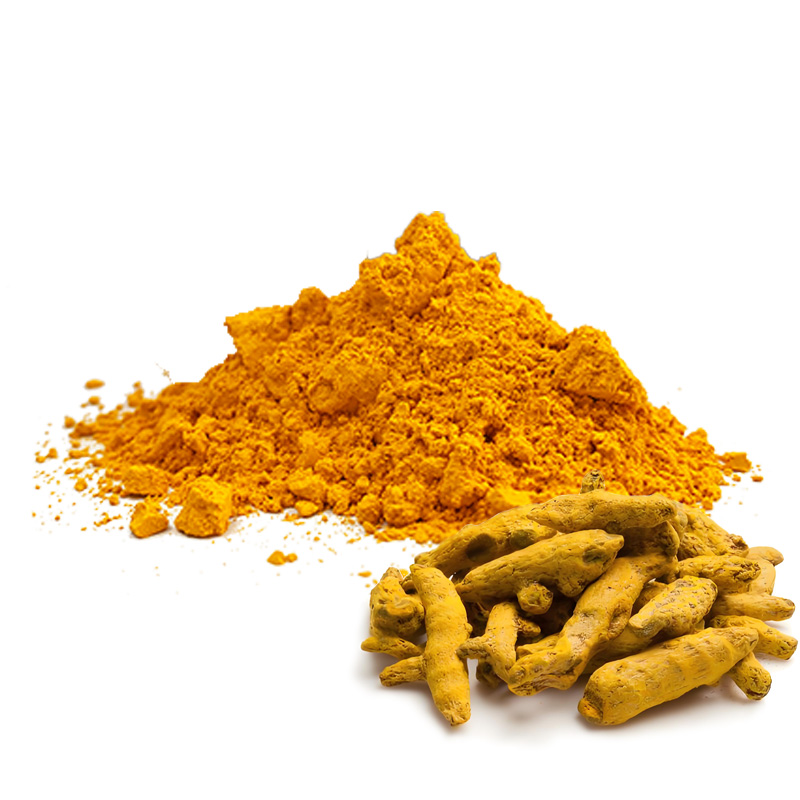

Turmeric Extract
-
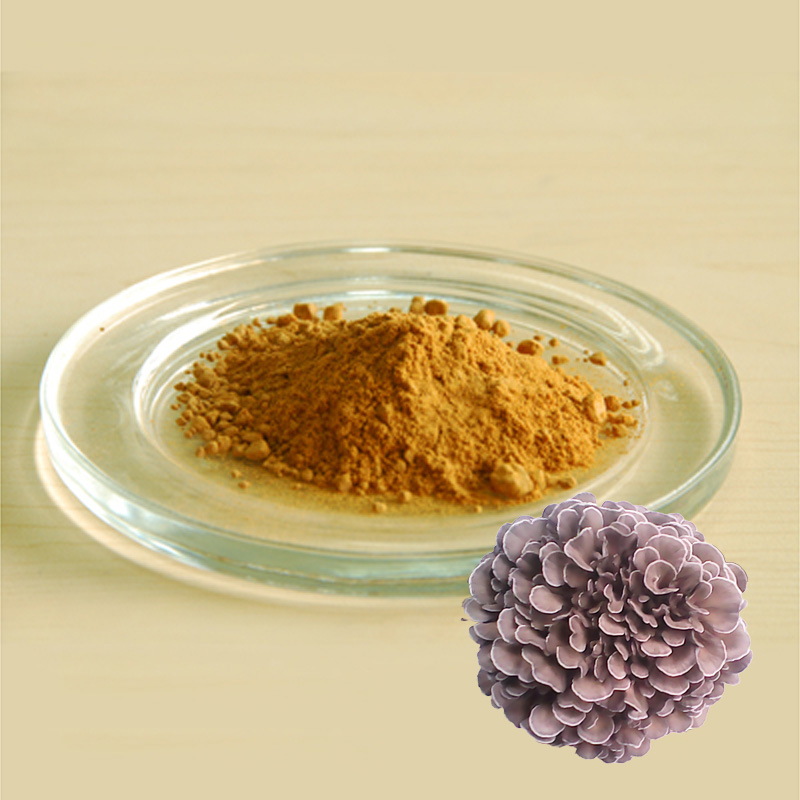

Maitake Extract
-
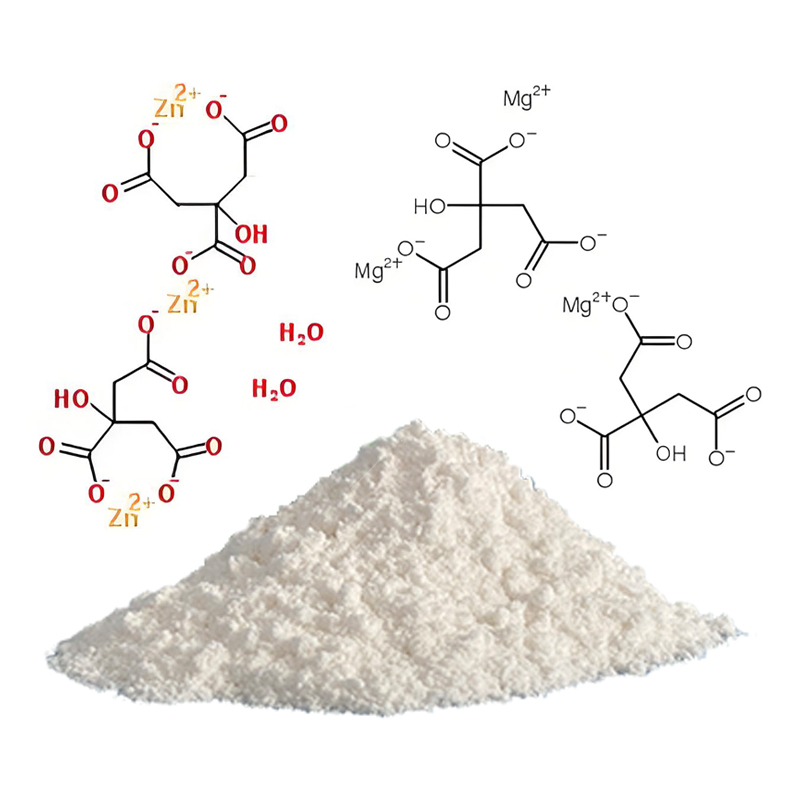
Citrate Mineral Salts
-
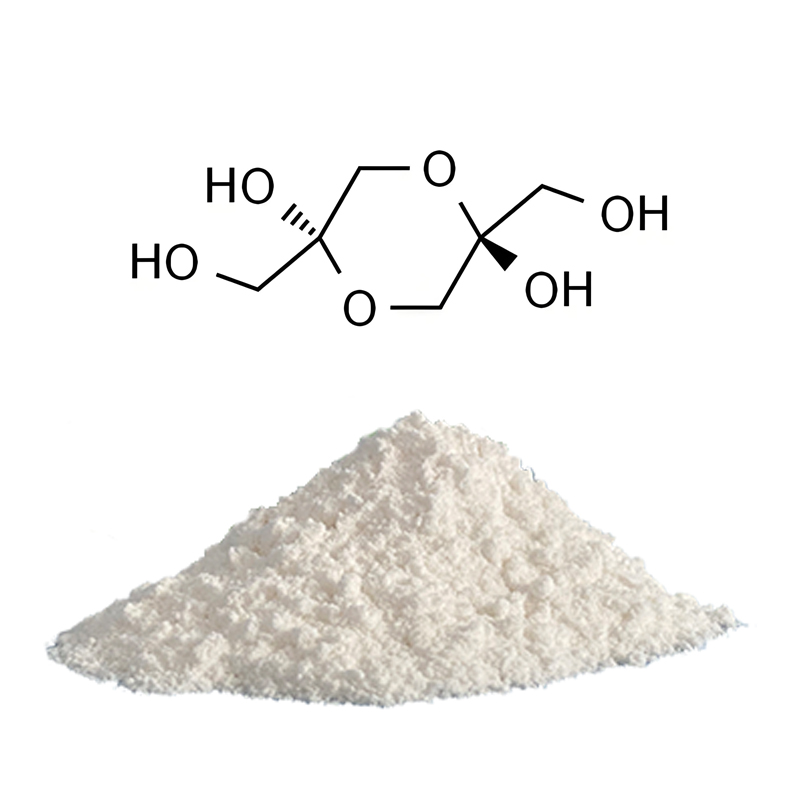
Dihydroxyacetone
-
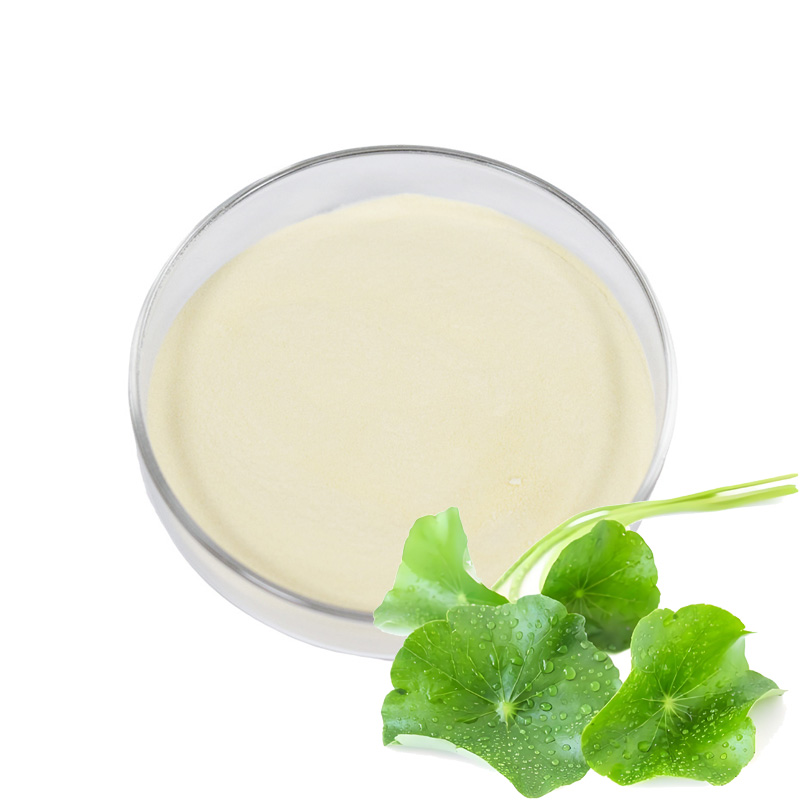

Gotu kola Extract
-
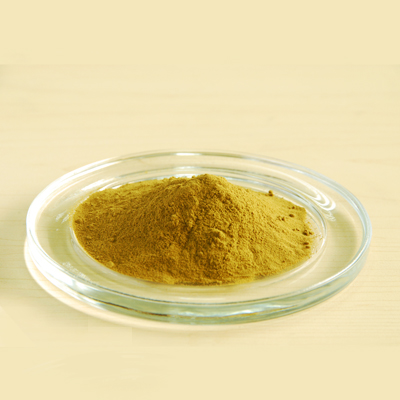

Gymnema Sylvestre Extract
-

Lychee Extract
-

Bamboo Leaf Extract
-

Diosmin
-

Sophora Japonica Extract(Rutin series)
-
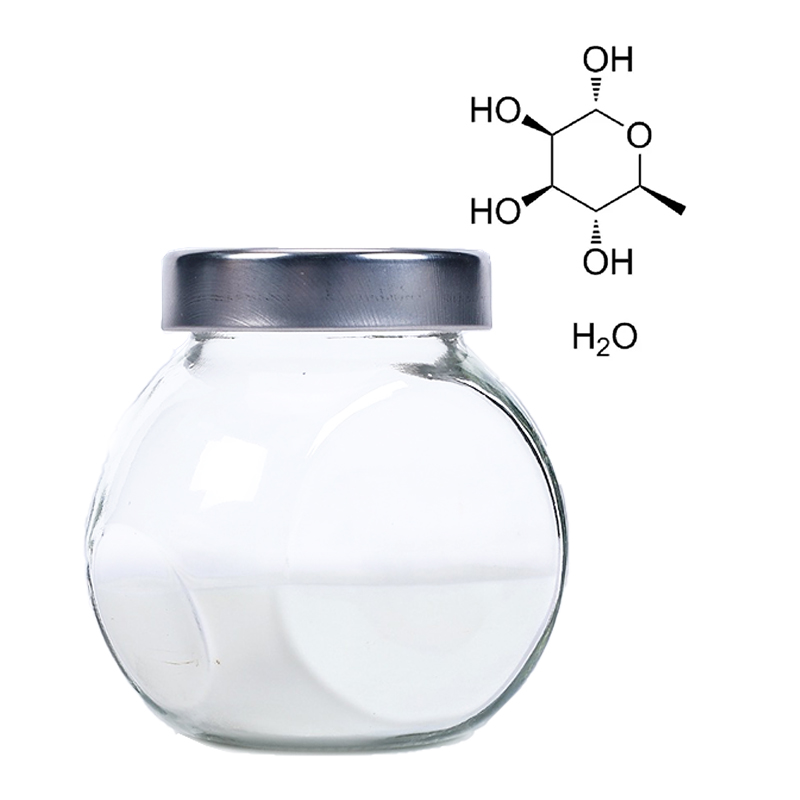
L-Rhamnose
-
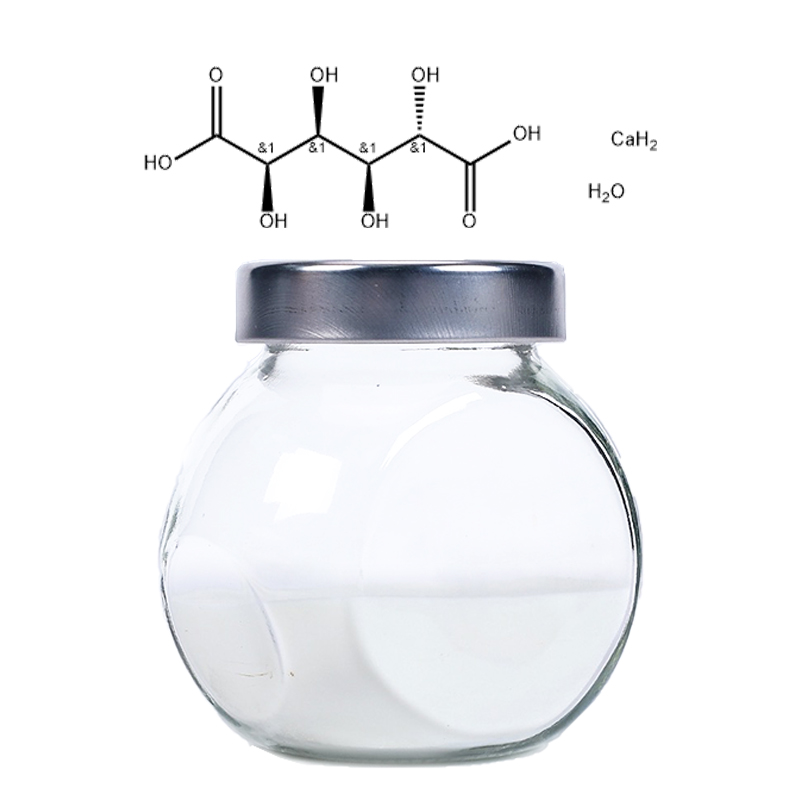
Calcium D-Saccharate Tetrahydrate
-

Artichoke Extract
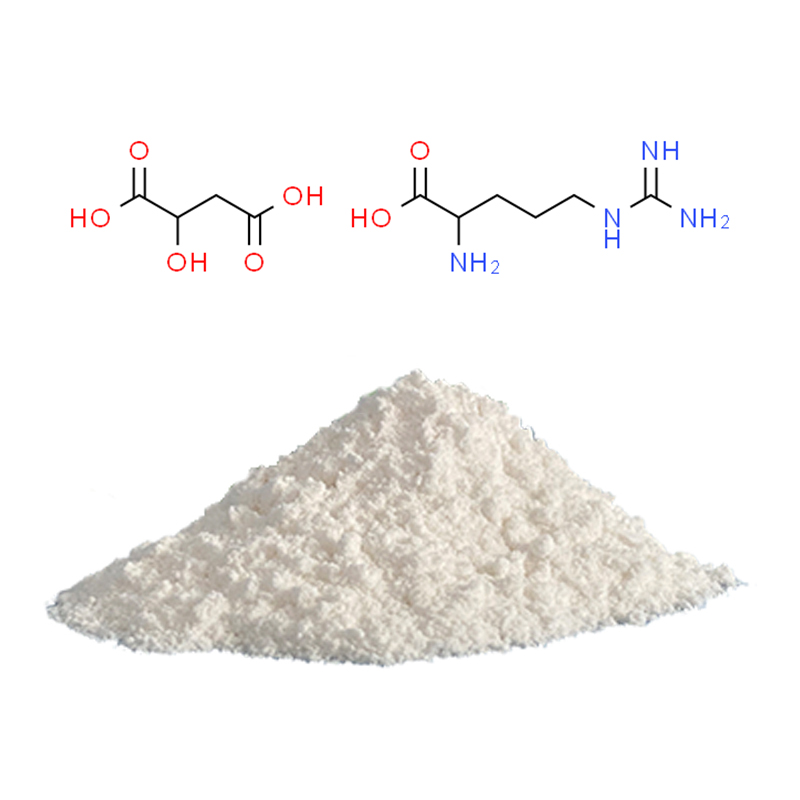
L-Arginine DL-Malate
- Alias: Arginine Malate
- Specification: 98.5% – 101.0% by HPLC
- Ratio:1:1,2:1
Описание
маркер
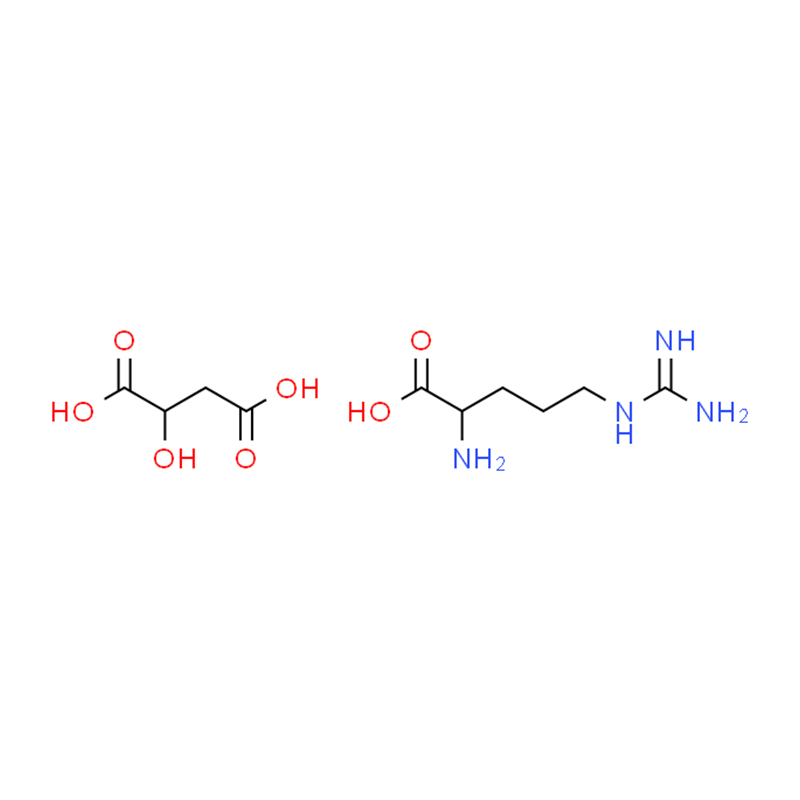
L-Arginine DL-Malate
- Alias: Arginine Malate
- Specification: 98.5% - 101.0% by HPLC
- Ratio:1:1,2:1
L-Arginine DL-Malate is a compound formed by combining L-arginine, an essential amino acid, with DL-malate, a salt derived from malic acid. This combination is widely used in various fields including sports nutrition, supplementation, and health care products. Below is a breakdown of its properties, uses, and considerations based on the details provided.
Malic Acid Overview
Malic acid, also known as hydroxybutanedioic acid, is an organic compound with the formula C₄H₆O₅. It exists in various forms, with three possible isomers:
- L-Malic acid(L-Apple acid)
- D-Malic acid
- DL-Malic acid(a racemic mixture of both L and D forms)
L-Malic acid plays an essential role in the human body’s tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), also known as the Krebs cycle, which is central to cellular energy production. The human body metabolizes only L-malic acid, while D-malic acid is not metabolizable.
Production of Malic Acid
- 1.Natural Sources:
L-malic acid naturally occurs in fruits such as apples, grapes, and lemons. It is also found in small amounts in some vegetables. However, the extraction of malic acid from these sources is challenging and expensive, making it unsuitable for large-scale industrial production. - 2.Synthetic Production:
In industrial settings, malic acid is typically produced via a catalytic process using fumaric acid. The resulting product is a mixture of both L- and D-malic acid (DL-malic acid), which is not metabolizable by humans. Therefore, while DL-malic acid is allowed as a food additive in several countries, there are concerns regarding its safety due to human metabolic limitations. - 3.Biotechnological Production:
Malic acid is now primarily produced using microbial fermentation, which ensures that only the L-form of malic acid is obtained. This method has largely replaced chemical synthesis for applications in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics
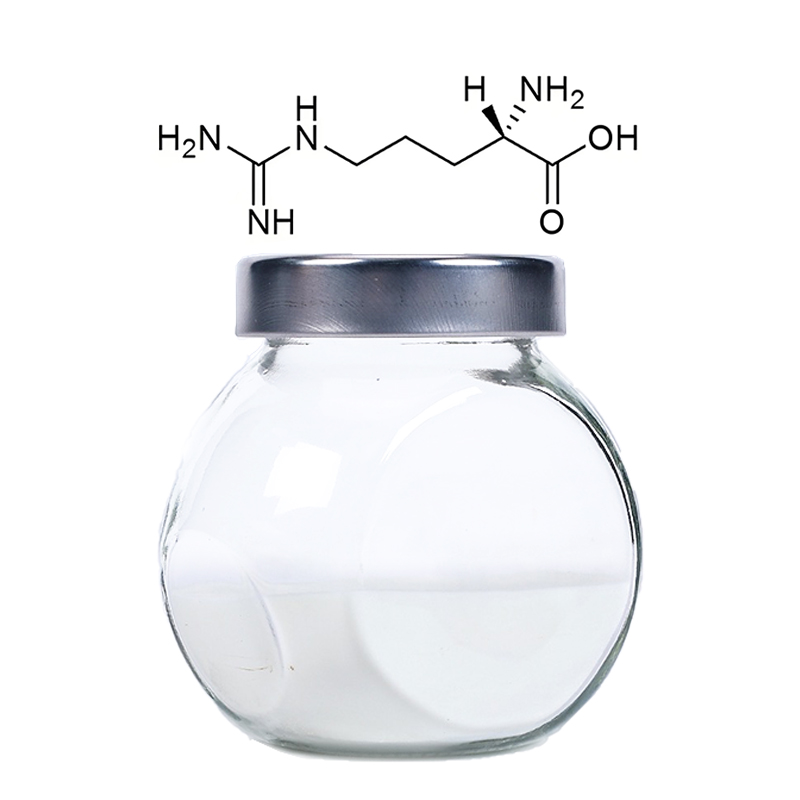
L-Arginine is an amino acid that plays a pivotal role in the production of nitric oxide (NO), a signaling molecule that helps in vasodilation, improving blood flow, and supporting various physiological processes. It is widely used for its potential cardiovascular and athletic benefits, including:
- Enhancing circulation: L-Arginine supplementation can improve blood flow by boosting nitric oxide levels, which may help reduce symptoms of conditions like high blood pressure, angina, and erectile dysfunction
- Supporting exercise performance: Athletes often use L-arginine to enhance performance by improving oxygen delivery to muscles, reducing fatigue, and increasing endurance